Understanding The Healing Power of Cannabis
Have you ever wondered why marijuana affects people the way it does? What is it that makes THC and CBD react within your bodies, while healing and offering relief to the ill? What makes this plant such a diverse medicine, able to treat such a large number of vastly different conditions?
If you had asked this question fifty years ago, there wouldn’t have been an answer for you to find. Unfortunately, the extraction methods available in the early 1900s made it difficult to determine which one of the 80+ cannabinoids found in cannabis was the psychoactive cannabinoid responsible for the effects of marijuana.
The truth is, it’s only been in the last couple of decades that scientists have truly even begun to understand the ways cannabis works within our bodies.
It all started with a scientific breakthrough in 1964, when a scientist from Israel named Raphael Mechoulam was able to identify and isolate THC for the first time – just prior to which they were able to identify CBD as well. Being able to isolate these cannabinoids for the first time was the first stepping stone in discovering the endocannabinoid system – a biological system that can be found in just about any living thing with vertebrae.
– “By using a plant that has been around for thousands of years, we discovered a new physiological system of immense importance,” says Raphael Mechoulam, the dean of the transnational cannabinoid research community. “We wouldn’t have been able to get there if we had not looked at the plant.”
In 1988, the first cannabinoid receptor was found in the brain of a rat. Initially found by Allyn Howlett and William Devane these cannabinoid receptors turned out to be plentiful in the brain – more so than any other neurotransmitter receptor. Soon after this discovery researchers started using a synthetic form of THC (which is actually FDA approved these days, to treat severe nausea and wasting syndrome) to start mapping the CB receptors in the brain.
Not much of a surprise, that the receptors were located primarily found in the regions responsible for mental and physiological processes including memory, higher cognition, motor coordination, appetite and emotions among other places. This would only begin to explain: how cannabinoids affect our brains and bodies – and it was becoming clear that cannabinoids likely played a larger part in our physiology than we ever expected. After all, why would we have cannabinoid receptors if cannabinoids could only be delivered from external sources?
It wasn’t until two years later in 1990 — before the next big breakthrough; when Lisa Matsuda announced at the National Academy of Science’s Institute of Medicine that she and her colleagues at the National Institute of Mental Health had managed to pinpoint the DNA sequence that defines a THC-sensitive receptor in a rat’s brain. Not long after this announcement they were able to successfully clone that receptor – allowing them to create molecules that “fit” or “activate” the receptors. Scientists were also able to develop genetically altered mice that lacked this specific receptor – meaning THC should have no effect on them.
When THC was given to the “knockout mice” as they were called, they found that because the THC had nowhere to bind, there was also no way to trigger any psychoactive activity – proving once and for all — THC works by activating specific cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system.
The answer to that question started to unfold in 1992, when the first endocannabinoid was discovered. Anandamide was the first, naturally occurring endogenous cannabinoid, or endocannabinoid. It was found by Raphael Mechoulam as well as NIMH researchers William Devane and Dr. Lumir Hanus.
Soon after, in 1993, a second cannabinoid receptor was found – as a part of the immune and nervous systems. Dubbed CB2 (the CB receptors in the brain officially dubbed CB1 receptors) receptors they are found to be plentiful – throughout the gut, spleen, liver, heart kidneys, bones, blood vessels, lymph cells and even the reproductive organs. However that curious, pesky question remained unanswered – why do we have cannabinoid receptors in the first place? (as named after the Sanskrit word for bliss.)
A second endocannabinoid was identified in 1995, discovered by none other than Mechoulam’s group yet again. This second major endocannabinoid was dubbed 2-arachidonoylglycerol or “2-AG” to keep it simple. This particular endocannabinoid attaches to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.
It was these discoveries, working backwards, tracing the metabolic pathways of THC, which allowed scientists to discover an entirely unknown molecular signaling system that resides within us – and within thousands of other biological lifeforms, basically everything on our planet with the exception of insects.
Due to the role cannabis had played in discovering this system it was rightfully named the endocannabinoid system. While we knew about the plant first – this cellular process has been happening within us for millions of years. According to Dr. John McPartland, the system started evolving as long ago — as 600 million years back – when complex life meant a sponge. There is evidence a possible 3rd CB receptor has still gone unidentified, thirteen years after the CB2 receptor was initially discovered.
Since we have found out the endocannabinoid system is responsible for maintaining many of our normal bodily functions – everything from helping to maintain healthy bone density (as found in a study with mice and the previously mentioned “knockout mice”) to naturally preventing diabetes – and that’s only the beginning. It’s interesting to see how far we have come. It has been 55 years ago THC had just been identified – thanks to the discovery of that one cannabinoid we’ve discovered an entire molecular system within our bodies that we never knew about.
Dr. Ethan Russo Explains the ECS!!!
Actually, the endocannabinoid system is possibly the single-most important system within our entire bodies – responsible for maintaining homeostasis. Basically, if our endocannabinoid system is out-of-whack, as your whole body could be at risk as it is responsible for many of our normal day to day functions. The possibilities that come with understanding the endocannabinoid system are practically endless.
This one system helps to regulate almost every aspect of our well-being – meaning if we can learn to manipulate these receptors (with use of cannabinoids from cannabis) we could possibly have the answer to not only curing diseases, however, preventing them all together.
The thing here is, this is still 100% true today, over 100 years later. There are thousands of brilliant men and women working in pharmaceuticals, working to create medicines to do exactly what cannabis is already capable of doing. Why do we (humans), always think we have a better way to do things?
Why do we have FDA approved drugs that mimic THC and are potentially stronger than naturally occurring THC – yet the plant that gave way to that drug is considered a highly dangerous drug with no medical value?
People are starting to see however, that sometimes, the best solution is a natural one. One that has been around and been used for thousands of years to treat conditions of all sorts. With the understanding of the endocannabinoid system comes the chance to bring the truth about cannabis to light – finally allowing us to understand how one plant can have such a positive impact on so many different ailments.
Now we’ve all got a good understanding of exactly how the endocannabinoid system was discovered through cannabis, it will be easier to understand — how the endocannabinoid system works – The Chemistry of Cannabinoids and the Human Body – also look at how cannabinoids THC and CBD lock-on to the CB receptors, in turn causing the medicinal benefits that people have come to trust over more traditional medicines.
–
It all started with a scientific breakthrough in 1964, when a scientist from Israel named Raphael Mechoulam was able to identify and isolate THC for the first time – just prior to which they were able to identify CBD as well.
Being able to isolate these cannabinoids for the first time was the first stepping stone in discovering the endocannabinoid system – a biological system that can be found in just about any living thing with vertebrae.
“By using a plant that has been around for thousands of years, we discovered a new physiological system of immense importance,” says Raphael Mechoulam, who is the dean of the transnational cannabinoid research community. “We wouldn’t have been able to get where we are today if he had not looked at the plant.”
How was the ECS discovered?
In the mid-1990s, Dr. Raphael Mechoulam also discovered the two main receptors that connect to both the endocannabinoids that our bodies naturally produce and plant-based cannabinoids like THC and CBD. These two receptors became known as cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid 2 (CB2) receptors. The breakthrough of these receptors required working backwards, tracing the metabolic pathways of THC that led scientists to discover the unknown molecular signaling system that exists inside these thousands of biological lifeforms.
What is the role of the ECS?
Rightfully named after the plant that aided in its discovery, the endocannabinoid system is a physiological system that controls and cares for your health. Endocannabinoids and its receptors can be found throughout the body, in the brain, organs, glands, and connective tissues. This system is actually responsible for also — helping maintain many of our bodily functions. It plays a crucial role from our immune system to our nervous system because endocannabinoids are often found at intersections of our bodies’ various systems, and it ultimately acts as a bridge between the body and the mind.
How does CBD benefit you?
The medicinal benefits that come from the proper use of CBD are seemingly limitless given the current science! CB2 receptors are mainly found in the immune system that binds with CBD and work as an anti-inflammatory agent for our body. There are immune boosting functions of CB2 that are activated by the proper use of CBD, which includes moderating the intoxicating effects of THC (aka psychoactive or high).
We hope we’ve answered a few of your questions on just why our products have such a positive impact on different aspects of your physical health. Stay tuned for more about the science behind our CBD products and how it can help with your specific needs! https://cannaisseurbrands.com/2017/09/01/endocannabinoid-system-part-1/
Endocannabinoid System Part 1 The ECS – YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=slq2yH7e91M
Endocannabinoid System Part 2 Terpenes – YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Iiy8zhcLtjY
How much THC for Cancer!!!!
It wasn’t until 2 years later in 1990 before the next big breakthrough; when Lisa Matsuda announced at the National Academy of Science’s Institute of Medicine and her colleagues at the National Institute of Mental Health had managed to pinpoint — the DNA sequence that defines a THC-sensitive receptor in a rat’s brain.
Not long after this announcement they were able to successfully clone that receptor – allowing them to create molecules that “fit” or “activate” the receptors. Scientists were also able to develop genetically altered mice that lacked this specific receptor – meaning THC should have no effect on them.
When THC was given to the “knockout mice” as they were called, they found that because the THC had nowhere to bind, and there was no way to trigger any psychoactive activity – proving once and for all that THC works by activating specific cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system.
However that curious, pesky question remained unanswered: Why do we have cannabinoid receptors in the first place?
In the article by Sulak on NORML.org, there was a quote he used that particularly stuck out to me… “There were never so many able and active minds at work on the problems of disease as now, and all their discoveries are tending toward the simple truth that you can’t improve on nature.” – Thomas Edison, 1902
The thing here is, this is still 100% true today, over 100 years later. There are thousands of brilliant men and women working in pharmaceuticals, working to create medicines to do exactly what cannabis is already capable of doing. Why do we (humans), always think we have a better way to do things?
Why do we have FDA approved drugs that mimic THC and are potentially stronger than naturally occurring THC – yet the plant that gave way to that drug is considered a highly dangerous drug with no medical value?
People are starting to see however, that sometimes, the best solution is a natural one. One that has been around and been used for thousands of years to treat conditions of all sorts. With the understanding of the endocannabinoid system comes the chance to bring the truth about cannabis to light – finally allowing us to understand how one plant can have such a positive impact on so many different ailments.
Do you need THC for Healing
FECO stands for Full Extract Cannabis Oil. RSO stands for Rick Simpson Oil. These are both anachronisms for CO (Cannabis Oil)…kind of. All CO is not the same. Some is made from only flowers, some from only trimmed discards mixed in with fan leaves and some from fan leaves only.
Some may have pesticide or toxic substance residuals depending on how the cannabis was grown and how the oil was made. FECO is made from both flowers and fan leaves, providing a full spectrum of all the good stuff the plant contains. The only fool proof way, in most situations, to ensure you get a high quality full spectrum oil is to make it yourself. Lots of links on the internet to steer/teach you. Also get organic cannabis, if all possible, as your raw material.
Though FECO and RSO can be somewhat the same thing in a lot of cases, the term “RSO” is refrained from many cannabis advocates vocabulary due to the use of these highly toxic solvents recommended by Rick Simpson. Benzene, Naptha, ISO alcohol and so on. If you can’t put it in your body, then don’t make oil with it.
CBD Isolate Vs. Full Spectrum CBD
What’s the Difference Between CBD Isolate vs Full Spectrum CBD?
Due to its non-psychoactive healing properties, Cannabidiol (CBD) has become a very popular option for patients — seeking a natural alternative to treat conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety, epilepsy, and more. As patients start to understand how CBD can be used to alleviate their symptoms, they are often faced — with a choice between using products made from CBD Isolate or Full Spectrum CBD. So, what exactly is the difference between the two?
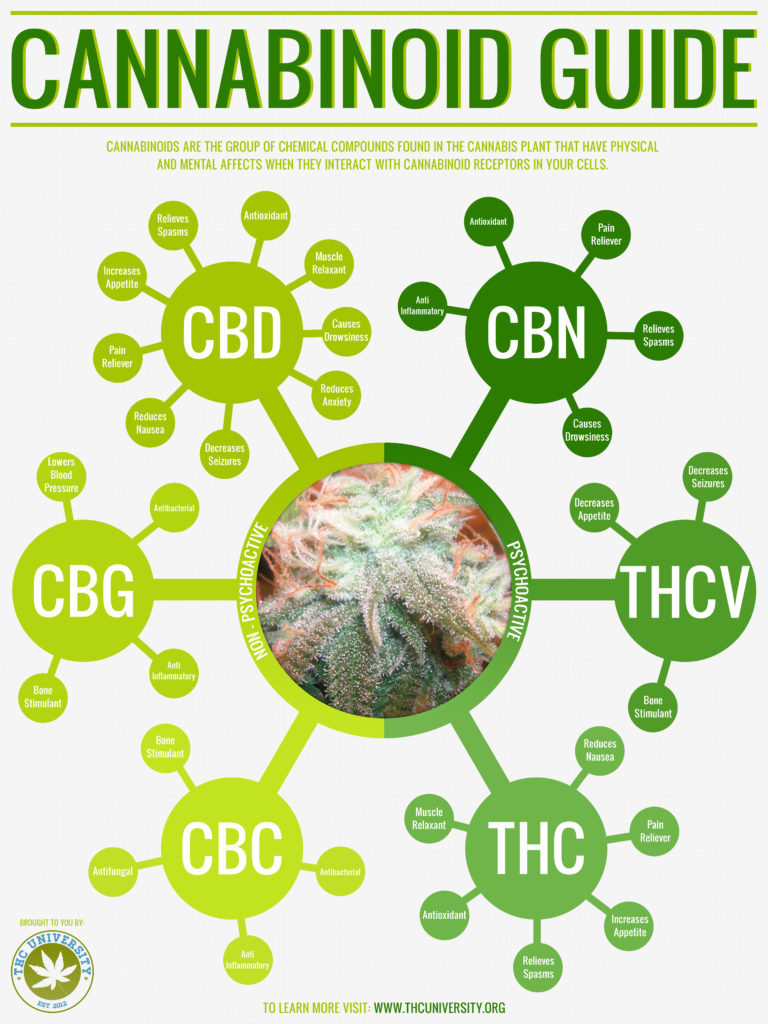
When CBD is referred to as full spectrum or whole plant CBD, it means that the CBD contains all other cannabinoids found in the marijuana plant including CBN (Cannabinol), CBG (Cannabigerol), and THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin), to name a few. And yes, along with these cannabinoids, Full Spectrum CBD also contains certain trace amounts of THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol), in very low concentrations (up to .3%), resulting in very minimal psychoactive stimulation.
CBD Isolate, on the other hand, is simply purified CBD that has been extracted from the marijuana plant and isolated from the other cannabinoids. So why is this important, and why would a patient choose one over the other? Let’s continue!
Understanding the Benefits of the Many Cannabinoids
As shown in the chart above, each cannabinoid offers different benefits for a wide variety of ailments. Notably, CBD offers most of the benefits of each cannabinoid combined. While there is no debate that CBD offers the most benefits compared to any single cannabinoid, many wonder if CBD alone is more effective for treating ailments than all the cannabinoids combined.
How Do You Make Cannabis Oil
CBD Isolate vs Full Spectrum CBD: Which is More Effective?
It was previously believed that CBD in its isolated form was more potent and concentrated than full spectrum CBD; however, in 2015, the theory was debunked by a study from the Lautenberg Center for General Tumor Immunology in Jerusalem. In the study, researchers administered full spectrum CBD and CBD isolate to 2 different groups of mice. When comparing the data of the two groups, the results proved that the group administered with full spectrum CBD were provided with higher levels of relief. Furthermore, the study demonstrated that full spectrum CBD continued to provide relief as the dose increased, while CBD Isolate did not provide the same effect when there was an increase in dosage. https://www.bing.com/images/search?q=full+spectrum+cannabinoids&FORM=HDRSC2
While full spectrum CBD has ultimately proven to be more effective than CBD Isolate and can also be used to effectively treat a wide variety of ailments, it does not discredit the effectiveness of CBD Isolate. There are a wide variety of situations when CBD isolate would be preferred over Full Spectrum CBD. For example, you may not necessarily need the full capabilities of Full Spectrum CBD, or if you aren’t legally allowed to use THC.
It is important to note — that other cannabinoids may cause negative reactions when isolated CBD wouldn’t (if the condition you are suffering from is critical, we definitely advise you speak to a medical consultant before trying out any version of CBD).
As researchers continue to study the marijuana plant, we will learn more and more about these amazing cannabinoids and what they can do for us. If you’d like to view current research on how CBD and the other cannabinoids benefit different conditions, visit the repository of medical research that covers over 50 medical conditions: https://www.alpha-cat.org/introduction-to-cannabinoids/ https://cbdorigin.com/cbd-benefits-many-conditions/